The Top 10 Most Forged ID Documents (2022)
Learn about the fraud trends of 2022 and how to protect your business in 2023.
Over the past year, Sumsub has analyzed half a million fraud attempts and narrowed down the 10 most commonly-forged documents. These include Vietnamese and Bangladeshi ID cards, as well as US driving licenses.
Check out this article to learn more about document forgery and penalties for it in different countries. You can also download Sumsub’s latest Fraud Report to learn about our fraud forecast for 2023.
What is document forgery?
Forgery is a criminal act in which a person falsifies or fabricates documents, or other objects,with intention to deceive and make profit.
Document forgery includes:
- creation of a fake document from scratch, or
- deliberately changing a genuine document in order to add, delete or modify information, while presenting it as genuine.
Forged documents can include photo substitution, data alteration, change in visas, or ID numbers, etc.
The most “popular” types of forgery include:
- Free hand simulation. When a person’s handwriting and/or signature is copied.
- Traced forgery. Reproduction of handwriting and/or signature using carbon or tracing paper, etc.
- Digital manipulation. Alteration of a document using photoshop and other kinds of software.
The spread of electronic documents has spurred forgery using photoshop and deepfakes. Digital manipulation has been on the rise in recent years, but the good news is that there is a choice of software solutions to keep you safe.
Suggested read: Liveness Detection: Choosing a Solution that Won’t Let Fraudsters in
Forged and faked documents
A fake document is a fabricated document (physical or electronic) which misrepresents a person’s identity, residency, finances, or employment, or otherwise misrepresents the document’s source, authenticity, or accuracy.
A forged document can be:
- either a real document (physical or electronic) which contains altered information
- A non-existent, or fabricated, document.
Suggested read: Document Verification
What are the 10 most forged documents
Based on our data more than 50% of all fraud detected worldwide is attributed to 5 countries:
- Bangladesh
- Pakistan
- Vietnam
- Nigeria
- USA
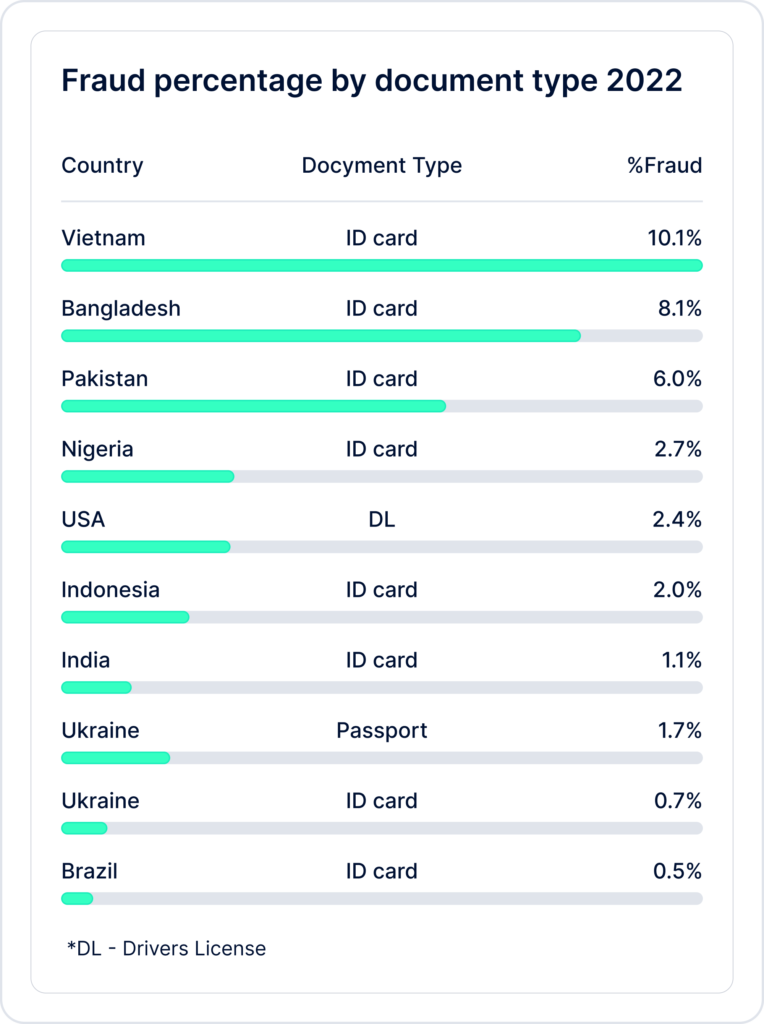
We recommend adding these potentially risky locations and document types to your list of red flags and paying extra attention to documents from these jurisdictions.
Why do fraudsters fake certain documents
Fraudsters fake documents from certain countries depending on existing loopholes, document security levels, and how often fraud occurs in a given jurisdiction.
Low document security. According to our report, half of the most forged documents were national ID cards. In some countries, these documents have fewer security features—watermarks, holograms, stamps—than documents intended for international travel, which makes them easier to forge.
For instance, India’s electronic ID card, the Aadhaar, can simply be printed out on paper. The document has almost no security features, except for a QR code. But, if a business’ verification system can’t read QR codes, it can easily miss a forged document.
Legal loopholes. Laws in some countries contain loopholes that allow criminals to forge documents without facing legal consequences. For instance, Article 327 of the Russian Criminal Code states that forgery or manufacture of any official document for the purpose of its use or sale is illegal. However, according to one of our in-house experts, there’s a loophole: if it can’t be proven that the forger planned to use or sell the fake documents, they cannot be prosecuted. Criminals use this loophole to falsify documents with impunity, and firms that forge documents operate in broad daylight.
Low privacy-awareness among citizens. Sensitivity around personal data privacy varies around the globe. In Europe, there’s a strict data protection regulation called the GDPR, and 67% of the EU citizens are aware of it.But the situation drastically changes in other parts of the word. Only half of the 54 countries in Africa have introduced data protection laws, leaving countless Africans helpless in the event of a data breach. In the absence of proper personal data protection rules, citizens are at greater risk of leaking their personal information onto suspicious websites that sell data on the darkweb.
Penalties for forging and falsifying documents
Forgery is considered a crime in all countries, but penalties vary from one country to another.
In the United States, for example, forgery is considered a federal crime in all states. The United States Code defines forgery as: “anyone, with intent to defraud, who falsely makes, forges, counterfeits, or alters any obligation or other security of the United States is guilty of a federal offense.” Forgery in the US is punishable by different penalties, depending on the state, including up to 5 years in prison, a fine of up to $25K, probation, and restitution (compensating the victim for money or goods stolen as a result of the forgery).
In the UK, according to Act 1 of the Forgery and Counterfeiting Act of 1981 the offense of forgery is defined as: “a person is guilty of forgery if he makes a false instrument, with the intention that he or another shall use it to induce somebody to accept it as genuine, and by reason of so accepting it to do or not to do some act to his own or any other person’s prejudice.” Penalties include fines, up to ten years in prison or both, depending on the offense, and types of documents forged.
In Germany, the crime of forgery is defined in Section 267 of the Criminal Code as “Whosoever for the purpose of deception in legal commerce produces a counterfeit document, falsifies a genuine document or uses a counterfeit or a falsified document shall be liable to imprisonment not exceeding five years or a fine.” In Germany even an attempt to forge a document is also punishable. The German Criminal Code specifies imprisonment sentences up to ten years, depending on the seriousness of the crime.
How to protect against forgeries
It’s critical to introduce a reliable document screening system that checks document security features and detects signs of graphic editing. Since some national documents have few security features and other weaknesses, businesses should add additional layers of protection:
Behavioral risk score uses device fingerprint analysis to track suspicious IP addresses and email domains, usage of VPN, and location mismatches.
Duplicate and blocklist search detects applicants that try to reuse data belonging to existing users. This stops fraudsters in their tracks by checking them against databases of banned persons.
Facial biometrics analyzes the facial features of an applicant to ensure that the true holder of the documents undergoes verification.
Check our Sumsub’s Fraud Report 2022 to make sure your business is safeguarded from fraud in 2023:

FAQ
-
What is a forged document?
A forged document is either a made-up fabricated document, or a real document (physical or electronic) which contains altered information to make it appear genuine. Forged documents can include photo substitution, data alteration, etc.
-
What are some commonly forged documents?
n 2022, the most forged documents are: Vietnamese ID card Bangladeshi ID card Pakistani ID card See the rest of the most forged documents in our Fraud Report 2022.
-
What is the most forged document?
In 2022, the most forged document is the Vietnamese ID card.
-
How can I tell if a document is forged?
The most efficient way is to use special document verification software.
-
What is a fake ID?
A fake ID is a fabricated ID document used to create a false identity.
-
What are the 3 most common forms of fake ID?
The three most common fake IDs are borrowed IDs, manufactured fake IDs, and forged IDs.
-
Can you pass KYC with a fake ID?
Although fraudsters are becoming more creative and use various means to trick KYC systems, a modern and sophisticated KYC solution can detect all kinds of fraud and, therefore, fake IDs.
Explore more
- Regulatory compliance
- Dec 21, 2023
- 10 min read
- Verification
- Dec 14, 2023
- < 1 min read





